A step-by-step guide to Richard Leeke’s TabGeoHack for creating your own filled maps in Tableau Software
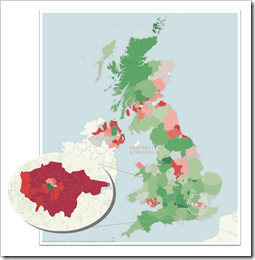 Way back in 2009, we had a beautiful guest post by Giedre Aleknonyte describing a workaround to generate Choropleth Maps with Tableau (using version 5.0 by the way).
Way back in 2009, we had a beautiful guest post by Giedre Aleknonyte describing a workaround to generate Choropleth Maps with Tableau (using version 5.0 by the way).
Those days are over. One of the major new features of Tableau 7 is Filled Maps (or Choropleth Maps as we used to call them in all blog posts here).
Did I say those days are over? Well, not quite. While Tableau provides filled maps down to the zip code areas in the United States, the level of detail in other countries is more or less rudimentary. In Germany, for example, you can create filled maps only for the 16 states (Bundesländer). This is nowhere near sufficient to do really compelling geographical data analysis and visualization. Up to now there was no way to do anything about it.
My friend Richard Leeke recently developed a fantastic tool called TabGeoHack which allows you to import literally any geographic level of detail of any region in the world into Tableau in order to use them for visualizations using filled maps. Richard is a co-founder of Equinox Ltd, a New Zealand based IT consulting firm and if you are a long time reader of this blog, you certainly already know him from the fantastic guest post series on Site Catchment Analysis. Even if you haven’t seen those articles, you probably know him from the Tableau Forum.
Surprisingly enough, Richard made his tool generously available for free in this Tableau Viz Talk post.
Please be aware that TabGeoHack – as its name suggests – is a totally unsupported hack utility, using an open back door of Tableau. The tool is a workaround with a certainly limited lifetime. It is beyond question that Tableau will provide similar built-in functionality with one of its next versions.
Richard was kind enough to grant me a sneak preview of TabGeoHack before publishing. Although the download includes a very detailed description and instruction manual, it took me quite a while to cut my teeth on the use of TabGeoHack. That’s why I thought it would be a good idea to write a step-by-step article on how to use TabGeoHack, including an example on Tableau Public, visualizing unemployment rates in Germany, broken down by counties, on a Filled Map.
So, do you want to create your own filled map of e.g. English counties, Spanish municipalities or even the individual sales regions of your company?
Here you go.
A Step-by-Step Guide to TabGeoHack
The following step-by-step guide is reduced to the max and only covers a very small part of all the possible settings and features of TabGeoHack. Its single purpose is to give you a quick start into how to use the tool and how to arrive at visualization in Tableau with filled maps not provided by the built-in geocoding. This article does not replace the detailed, comprehensive instruction manual Richard provides.
This post is just a jump start into using TabGeoHack. No more, no less.
Step 1 – Download and install TabGeoHack
Download TabGeoHack and unzip it to a folder on your local drive. This could be any folder on your hard disk. To keep it as simple as possible, I used C:\TabGeoHack in the example below.
Note that at this point in his detailed instructions Richard suggests that you add TabGeoHack to your system PATH so that you can run it from anywhere. This might be worthwhile if, like Richard, you have lots of different sets of custom geocoding files which you want to store in the folder structure for the projects they relate to. Personally, I prefer to keep it simple, store all my YAML configuration files in the TabGeoHack directory and always run it from that location – that way I didn’t need to modify my system PATH. So these instructions assume you have not put it on the PATH.
Step 2 – Download and install GDAL
TabGeoHack requires a publicly available geographical library called GDAL (Geographic Data Abstraction Library). You can download it here: GDAL 1.9. Save the zipped folder to your local drive and unzip it to a folder. I copied the files to the following path: C:\GDAL Mapserver.
Step 3 – General settings
Let me start this section with a brief aside: The YAML File Format
TabGeoHack uses YAML files for general configuration and for settings related to each set of geocoding files. YAML is a markup language and I will not go into the details here. One reason is that I do not know anything about it. More important, however you do not need to know much about it either to use TabGeoHack.
All you need to know in the first step is the fact that YAML files are text files and basically you can open and edit them with any given text editor.
However, YAML heavily depends on correct textual indentation. And YAML expects spaces used for indentation, not tabs. If you are using a standard text editor like Window’s NotePad, you should choose a font with a fixed width like Courier New.
The best and easiest way of editing the TabGeoHack configuration files is using an editor which understands and supports YAML, like the free NotePad++ or Scite.
Within the folder C:\TabGeoHack you will find a file called tabgeohack.yml. In my example set-up, TableauGeoHack.yml has to look like this:
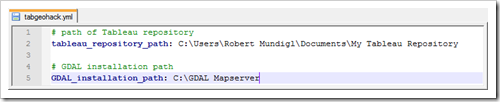
All you have to change here is the text in black. Set the path of your Tableau Repository and the GDAL path, i.e. the folder you copied the GDAL files to in Step 2 (C:\GDAL Mapserver in my case).
Step 4 – Find and download spatial files
In the next step we have to bring the spatial files to the process.
TabGeoHack can basically handle any polygon spatial data format as long as it is supported by the Geographic Data Abstraction Library (which we downloaded and installed in step 2). ESRI format is the most commonly found data format and the only format I have tested so far.
A search string in Google like “ESRI Shape Files download” will point you to a variety of resources providing Shape Files for download.
One of the most comprehensive sites I have found is Global Administrative Areas, including the ESRI Shape Files of all administrative regions of all countries in the world. In my own example here, however, I used a different resource: Geodatenzentrum, because those shape files already include the same IDs of the counties (Kreise) I had in the data source I wanted to visualize with Tableau.
The files for download are usually zipped folders, containing several different files. The following 4 file types are the crucial ones you need for TabGeoHack: DBF, PRJ, SHP and SHX. The zipped folder I downloaded from Geodatenzentrum includes those 4 files for 4 different administrative regions: Bundesland (state), Regierungsbezirk (district), Kreis (county) and Stadt (city):
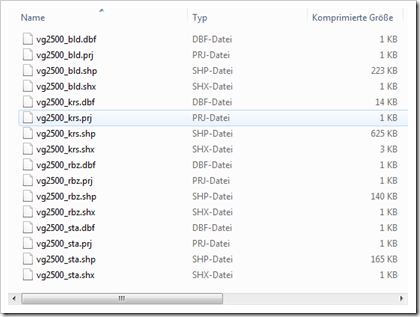
Create a new folder within your TabGeoHack folder, e.g.C:\TabGeoHack\Germany and copy your shape files to it.
Step 5 – Create your own YAML configuration file and change the main settings
We have the shape files now, but we do not know much about the data they include. Thus we need to explore the content of the shape file. Before we can do this, we have to create a YAML configuration file to give TabGeoHack the information needed to access and analyze the shape files.
The TabGeoHack download comes with an example YAML file (“Porirua Tsunami Warnings.yml”) and a generic template (“geocoding_template.yml”) where Richard provides a very detailed description of all sections of the configuration file in his comments.
Copy one of those files to C:\TabGeoHack, rename it (germany.yml in this case) and open it. For this step you can ignore most of the lines. This is an example of the bare minimum you need to have in your file:
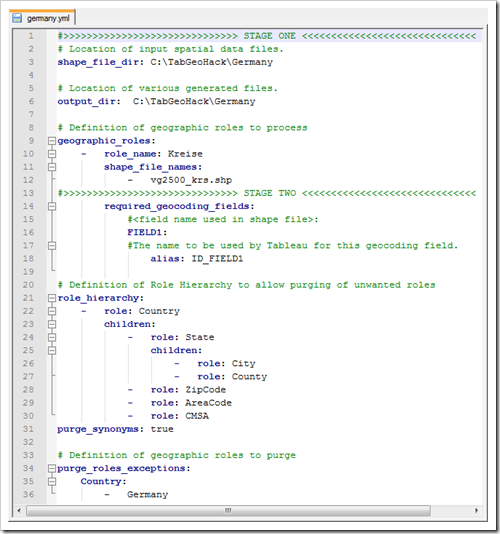
Here is what you definitely have to change:
Line 3: Specify the directory where you copied your shape files to in step 4
Line 6: Specify the directory where you want to store the output files of TabGeoHack. To keep it simple, we are using the same path as in line 3
Line 10: Specify the name of the geographic role. In this example, we are using “Kreise”, the German word for counties.
Line 12: The shape file name (the file including the extension SHP for ESRI format or whatever extension applies if you are using other spatial file formats)
Another brief aside: The DOS Command Prompt
TabGeoHack has no fancy user interface. You have to run it from the DOS command prompt. The command prompt is a native Windows program which lets you run programs without a user interface. I suspect many of you rarely, if ever, use it. Don’t worry if you are not familiar with it. It is pretty easy. Here is what you need to know:
- In the Windows Explorer, keep the SHIFT key pressed and right click on the TabGeoHack folder. From the drop down select “open command window here”. A new window will pop up and this is where you have to run the tool:
The shift right-click shortcut works with Windows 7 and as far as I know also with Windows Vista. If the shortcut is not available on your system, go to the Windows start menu, click on Run and type in cmd.
- If you don’t have the shortcut described above, you need to navigate to your TabGeoHack directory first. You can change the directory by using the DOS command cd (change directory, e.g. cd C:\TabGeoHack). Cd.. takes you one level up in the directory hierarchy and cd \ brings you to the top of the directory tree (i.e. C:\).
- Simply type the commands described in the next steps.
- Pressing Enter runs the command you typed.
- You can navigate within the command line using the left and right arrow keys, the HOME and END key.
- You can use the arrow up and arrow down keys to loop through the commands you already entered earlier.
That’s pretty much it. For our purposes you do not need to know more about the DOS command prompt.
Step 6 – Analyze the fields in your shape files – the info option
In the command window run TabGeoHack with the –info option for the file germany.yml:
tabgeohack –info germany.yml
You get the following result:
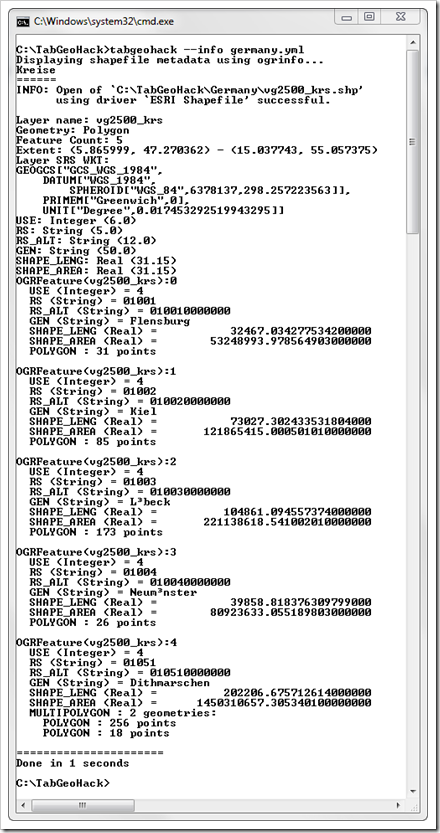
TabGeoHack provides some information on the spatial file itself, like the geometry, the coordinate reference system and others. More important to us are the following fields of the shape files and the first 5 data sets. From this information we can easily see which field contains which information. Counties in Germany (Kreise) are usually identified by a 5 digit ID (Kreisschlüssel), i.e. the field RS in the spatial file is this ID. GEN contains the real names of the counties like Flensburg and Kiel. So, what we need in our custom geocoding are the fields RS and GEN.
Step 7 – Define the required geocoding fields in your YAML file
Knowing (or at least assuming) the relevant data fields, we now have to complete the configuration file germany.yml. In the end it will look like this:
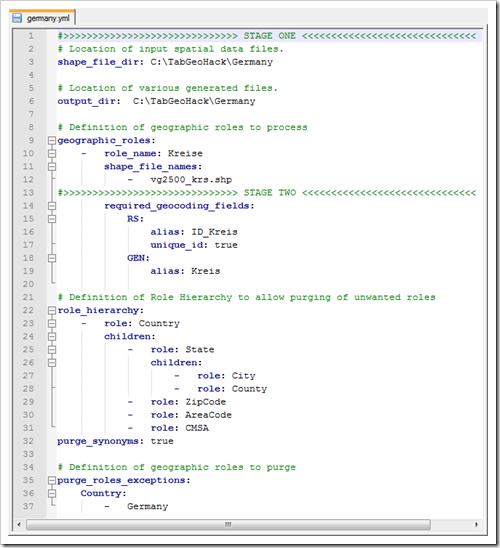
What we added to the file created in step 5 is the following:
- In lines 15 to 19 we define the required geocoding fields identified in the previous step: RS and GEN. We specify RS as the unique identifier and aliases for the fields which are easier to understand.
- In the section purge_roles_exceptions (line 37) we say that we wish to purge at the level of country (which implicitly purges all roles beneath country) and we define Germany as the only exception – that is we keep Germany and all data related to Germany (in case we want to use the built-in geocoding data for Germany in our viz). We are purging all the other countries in order to minimize the size of the custom geocoding and to maximize Tableau’s performance. Purging also helps to minimize the file size of a packaged workbook and thereby the usage of your Tableau Public storage.
Please be advised that purging is an important factor. You can easily try to load too much detailed map data which would result in either poor performance or Tableau running out of memory. Please consult the TabGeoHack documentation for more details on how to avoid this, including how to simplify complex boundaries with too many points.
Important note:
Please be advised that purging the way described above removes all other geographical information. As long as you have your custom geocoding in place, geographical visualizations for other regions (like the United States) will not be possible. This applies to already existing workbooks and to new ones. It also applies to packaged workbooks.
To make them work again, you have to remove the TabGeoHack custom geocoding from Tableau (Map | Geocoding | Remove Custom Geocoding). You can easily and quickly add it back when you need it with another TabGeoHack option: –activate.
Step 8 – Generate the input file for custom geocoding – the roles option
After completing the configuration file, we can now let the tool create the database for the custom geocoding (the –roles option):
tabgeohack –roles germany.yml
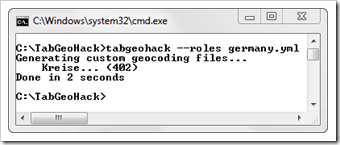
Richard’s tool is extremely fast. Within only 2 seconds it created the CSV we can use for importing the custom geocoding into Tableau. However, be aware that the time TabGeoHack takes to finish one of the steps depends on the spatial files and the size of the custom geocoding. Creating custom geocoding files for all postal zones in Australia, for instance, can take up to 30 minutes or more. So, if TabGeoHack seems to be stuck for a couple of minutes, please be patient. If there is a problem, the tool will throw an error. As long as it doesn’t, it is probably just still busy.
Before importing into Tableau, let’s have a look at the file first. It is stored in the following directory:
C:\TabGeoHack\ Germany\Custom Geocoding Files
and it looks like this:
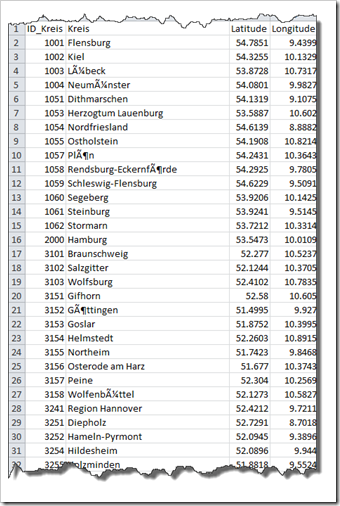
The file contains the fields we specified using the aliases as the field names (ID_Kreis and Kreis) and the latitudes and longitudes of the centres of the shapes. All we need for importing the custom geocoding to Tableau.
Don’t let the strange characters in some of the strings confuse you. Those are substitutes for the so called German Umlaute (ä, ö, ü). We do not have to take care of this, though. TabGeoHack will do all the work for us in the background.
Step 9 – Import custom geocoding into Tableau
The next step is simple and I bet most of you have already done this before: Import the custom geocoding into Tableau.
Open Tableau and create a new workbook (New | File). You do not have to connect to a data source. We will only import the custom geocoding and do not yet need a data source.
From the main menu select Map | Geocoding | Import Custom Geocoding. Browse to the folder containing the CSV we created in Step 8 (C:\TabGeoHack\Germany\Custom Geocoding Files) and click OK.
After Tableau finished the import, simply close Tableau. It is important that all copies of Tableau are closed before running the next step.
Step 10 – Associated shapes and custom geocoding – the shapes option
We are almost there. We have the custom geocoding in Tableau, but we do not have the shapes assigned to it. Thus, we have to run TabGeoHack again, this time using the –shapes option:
tabgeohack –shapes germany.yml
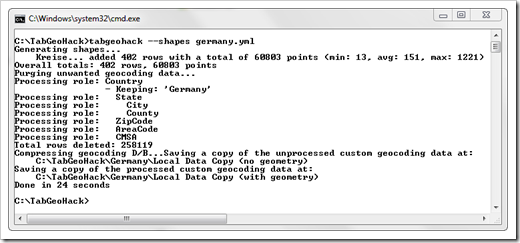
That’s it.
TabGeoHack can call it a day now.
Step 11 – Get your data source ready
However, we can’t. Not yet. We want to see the new filled maps for Germany’s Kreise, don’t we? So, let’s grab some data. Here is a database with figures of civilian labor force and unemployed by German counties (Kreise) from October 2009 to October 2011:
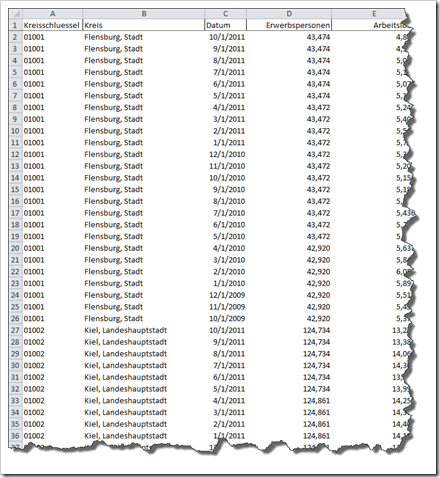
As mentioned already in step 4, I was lucky enough to find shape files with an ID that matched the IDs in the data source I wanted to use for my visualization (standard ID of Germany’s Kreise).
Sometimes, however, you will have to map the IDs in your own data to the IDs used in the custom geocoding created by TabGeoHack. This is yet more work, but usually not a big deal to create a mapping table or to enhance your data set with an additional field containing the custom geocoding IDs.
Step 12 – Use custom geocoding in your Tableau workbook
Open Tableau and connect to the data source (the German labor force / unemployment database).
In the data window, right-click on Kreisschlüssel (ID of the county) and select Geographic Role. You will notice that the custom geocoding created a new entry in the list of geographic roles: Kreise. This is exactly the name we specified in germany.yml. Click on Kreise and select ID_Kreis. This makes the connection between the dimension Kreisschlüssel in our database and the field ID_Kreis in the custom geocoding. This way, the shapes are assigned correctly to the values in the database:
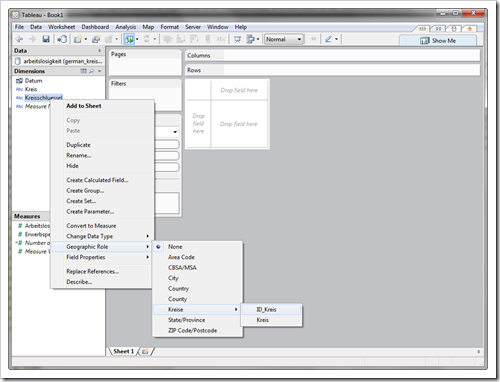
Next, drag Kreisschlüssel to the Level of Detail Shelf, select filled maps as the Mark Type and you can already see the map of Germany divided by Kreise:
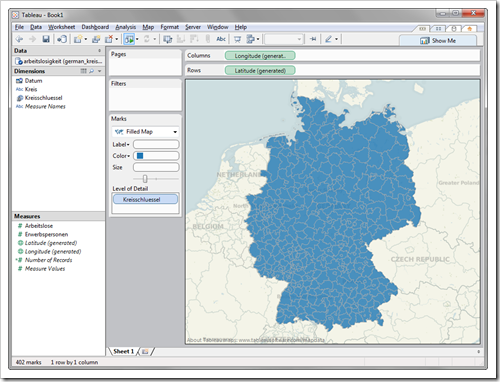
You see: it works. 12 steps and you are good to go. Create filled maps on any level of detail. All you need to do is to find the shape files and to go through the step-by-step process described above.
Example on Tableau Public
Enough storyboarding. Let’s shoot something.
Using the German unemployment database and Richard’s fabulous TabGeoHack tool, I created the following visualization:
The visualization is hopefully self-explanatory. Here are just a few hints:
- The visualization has 3 tabs: filled maps by counties, districts and states. Compare the maps and you will easily see how much more insight the map by counties provides into the geographical distribution of the data compared to the map by states.
- Use the month slider filter to walk through the period from October 2009 to October 2011.
- The state filter gives you the option to get down to one selected state. Please note that this is filtering the data and not zooming into the map. Thus, the color range and the fill colors will change. Filter by Bavaria, for instance, and you will see what I mean.
- Of course the map is fully functional, i.e. you can zoom in and out, pan around by shift click, the tooltips are working, etc.
There is much more…
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, TabGeoHack offers many more options and settings, way more than I am able to cover in this guest post. Here are just 2 examples:
- You can use more than one instance (i.e. shape files) within one custom geocoding. This is what I did in my example posted above on Tableau Public. The custom geocoding includes the districts (Regierungsbezirke) and counties (Kreise). You can include both geographic instances by simply inserting one more role instance in your YAML file.
- If you need to create more than one instance of custom geocoding (e.g. for different countries) and you want to switch between them, TabGeoHack offers the –activate option to do so. Please refer to the manual for further details.
So: please be aware of the fact that this post does not cover all the functionality of Richard’s tool.
This post is not intended to replace the instructions Richard provides in his manual. It was only supposed to be a heads-up and a step-by-step guide into TabGeoHack. Please read Richard’s manual thoroughly and you will find all the other features fully described.
International Issues
If you are working with a Windows language version other than English, you have to take care of a few things in order to make the process of creating your own filled maps with TabGeoHack as smooth as possible:
- Change the Date and Number format settings of Windows to English (Start button | Control Panel | Clock, Language & Region | Format Tab and select English from the drop down list). This is necessary because the CSV created in step 8 is in English format, i.e. commas as the field separators and decimal points. In German and other European countries you have semicolons as field separators and a comma as the decimal separator. If you are not switching to the English number format, you will get problems during the import of the custom geocoding.
- If you are using a German or French version of Tableau, switch to the English user interface (Help | Choose Language). This is necessary because if you are using e.g. German as the interface language, Tableau expects to find fields called Breitengrad and Längengrad in the CSV. TabGeoHack, however, creates the CSV with Latitude and Longitude as the column headers.
- Since Tableau 7, the folder names in the Tableau Repository are in German if you are running a German version of Windows or in French if you are running a French version. The folder containing the custom geocoding is called Local Data in English, Lokale Daten in German and Données Locale in French.
German users have the option to add the following line to the configuration file created in step 3:
tableau_country_code: DE
If you do so, you do not have to take care of the different folder names.
In French, however, Richard didn’t manage to get this working. The workaround is very simple. After you have done the import of the custom geocoding into Tableau and before your run TabGeoHack with the –shapes option, you rename Données Locale in your Tableau Repository to Local Data. Don’t forget to rename it back to Données Locale after TabGeoHack is finished and before you open Tableau again.
After you finished your work with TabGeoHack, you can turn back the number format and the Tableau interface language back to your own language.
You see: a few more little things to know and take care of if you are outside of the English language area, but no big deal.
Warnings
TabGeoHack is in fact a hack. Brilliant, no doubt about it, but still a hack and totally unsupported:
- Don’t expect any support from Richard if it doesn’t work for you. If you run into a problem, you can leave a comment on Richard’s Tableau Viz Talk post. Richard will keep an eye on the discussion going on there. No promise or commitment, though.
- Don’t expect Tableau to support anything created using this tool. They probably would not even know what you are talking about.
- Any future release of Tableau (even a minor one) could stop TabGeoHack altogether. Even a custom geocoding setup you had created previously. Don’t rely on your workbooks using TabGeoHack custom geocodings to work forever.
- No warranty. Neither Richard nor I will be liable for any errors or problems arising from the use of TabGeoHack.
In a nutshell: use it with caution. If you are creating a Tableau workbook you are desperately relying on, refrain from using a custom geocoding created by TabGeoHack.
An Alternative: ShapeToTab
If you don’t want to use the custom geocoding produced by TabGeoHack, you can still fall back on the polygon workaround for filled maps with Tableau: Polygon Files Structure. The basic idea is adding polygon data of all geographic regions to the data source and using Polygon as the Mark Type and the polygon data field on the Path Shelf. Until version 6, this workaround has also been described in the manual. The only problem was getting one’s hands on the polygon data.
This problem is solved now. Almost as a by-product, Richard has provided another awesome tool: ShapeToTab.
The use of ShapeToTab is very easy:
- Download ShapeToTab and unzip it to a new folder on your local drive
- Download the GDAL library (see step 2 above, if you haven’t already for TabGeoHack)
- Edit the configuration file called shapetotab.yml. This file only has one line in, specifying the path to the GDAL folder (comparable to step 3 above)
- Copy the spatial data file (e.g. vg2500_krs.shp in the example above) to the ShapeToTab folder
- Open the command prompt and type
shapetotab vg2500_krs.shp
The tool will then create 2 CSV files in the ShapeToTab folder, one with the feature data and one with the polygon points.
That’s it.
Last, but not least
A big time thank you very much goes to Richard Leeke for developing and sharing this fabulous tool. I have no clue how Richard managed to get this far with TabGeoHack. This is really impressive. I am feeling very honored that Richard let me have a sneak preview and to allow me to post about it on Clearly and Simply.
Many thanks, Richard!
If you find TabGeoHack useful for your own work, please drop Richard a line of thanks here or on his Tableau Viz Talk post.
Many thanks go also to Shawn Wallwork who thoroughly tested TabGeoHack before publishing and helped Richard to track down some bugs. Richard told me that Shawn also came up with a lot of very helpful ideas for improvement. Many thanks for your time Shawn.
What’s next?
The still missing parts of Sheel Bhatiani’s guest post series “Expand your Reach in Tableau with Parameters” and other Tableau and Excel articles will come soon.
Stay tuned.
Leave a Reply to Daan (Infotopics) Cancel reply