How to create a Microsoft Excel Pivot Table lookalike Crosstab with Texts in the Value Area using VBA
 The recent post showed a way how to create a Pivot Table lookalike crosstab with texts in the value area.
The recent post showed a way how to create a Pivot Table lookalike crosstab with texts in the value area.
However, due to the fact that it was restricted to Excel formulas, the approach came with a couple of drawbacks. Using formulas forces you to define the layout and the size of the crosstab in advance in a static structure. It goes without saying that this considerably limits the usability in real life.
Without VBA, there is no way out. However, some VBA helps to overcome almost all of the disadvantages of the formula based approach. Today’s post is the announced follow-up: it describes how to use VBA to emulate a Pivot Table lookalike crosstab with texts in the value area, as always including the Excel workbook for free download.
The Idea and Concept
The basic idea is a fixed and named cell range on a separate worksheet steering the layout of the crosstab, i.e. the definition which data field goes to which part of the crosstab (value area, rows, columns and filter).
Everything else is done by a VBA routine analyzing the raw data and creating and formatting the crosstab. This routine is executed whenever something changes (data, layout definition or filter).
The crosstab will
- show only the relevant category entries in the rows and columns
- display filter, row and column category entries sorted ascending
- display the texts in the value area as values (no formulas)
- include an automatically created dropdown (form control) as the filter input control
- automatically be formatted
The Preparation of the Workbook
Although we will have the VBA routine to do the laborious work, we still need a little bit of preparation of the Excel workbook:
- Bring your data into your workbook. We are using the same fictitious example data of a project risk list again
- Define a name for the cell range containing the data (“myData”)
- Insert an additional worksheet [Control]. Here is an example screenshot:
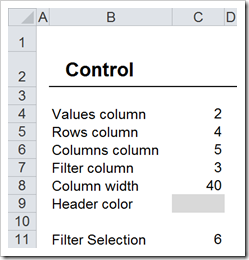
Columns C4:C7 define the layout of the pseudo Pivot Table. The numbers represent the column numbers within our data table. In the example shown above, the data from column 2 of the data table (the risk description) will be displayed in the value area of the crosstab, the data from column 4 (the impact) will go to the rows of the crosstab, column 5 (the probabilities) will be displayed in the columns of the crosstab and column 3 of the data table (the risk type) will be used as the filter. If you want to change the layout of the crosstab later, we do not have to change the VBA code. Instead, we simply change these 4 values. A combination of 2, 3, 4, 5 will bring the risk types to the rows, the impact to the columns and use the probability as the filter.
In cell C8 we define the width of the columns of our crosstab and in C9 we select the fill color for the row and column headers of the crosstab.
Cell C11 stores the actual selected filter.
- Define names for the range B4:C9 (“myPivotTableDefinition”) and for C11 (“myFilterSelection”) in order to be able to address these cell ranges in VBA.
- Finally insert a new worksheet [Pivot Table Risks] and assign a name to the top left cell of our pseudo Pivot Table (“myPivotTableStart”).
The Implementation – The VBA
I think I don’t have a snowball’s hope in hell to describe and explain the VBA code line by line. I did my very best to write readable and comprehensible code (not sure if I succeeded) and added a few comments. Thus, I will restrict myself to a few hints on the general structure of the VBA:
There is only one single module in the workbook containing 2 main functions and 2 main subs:
- The function UniqueItems returns a list of unique items from an array of values
- The function FindPosition does pretty much the same as the worksheet function MATCH. We could use Application.WorksheetFunction.Match(..) instead, but the VBA is faster than calling the worksheet function
- The sub QuickSort sorts an array ascending
- The sub CreateTextPivotTable – this is the main procedure
The sub CreatePivotTable consists of the following main steps:
- Initialize the data structure and transfer the data and the Pivot Table definition from the worksheets to VBA variables
- Delete the existing Pivot Table, unmerge cells, clear all formatting and delete the existing filter drop down
- Prepare the filter: create a list of unique entries in the data field selected as the filter, add the entry “All” and create a filter dropdown on the worksheet
- Detect the row and column headers by creating lists with unique items from the data fields selected for rows and columns
- Loop through all data rows, detect their position within the crosstab (which row / which column) and calculate the number of entries in each field of the crosstab matrix
- Calculate the maximum number of entries per row category
- Write the crosstab to the worksheet
- Format the crosstab
- Update the named formula "myPivotTable"
- Clean-Up (deallocate the data structure)
The code will always delete the existing crosstab and create a new one from scratch. It has to be updated if
- … the data is changed or new data rows have been added
- … the definition of the layout on worksheet [Control] has been changed
- … the user changed the filter by using the dropdown
The update of the crosstab after changing the filter is managed within the VBA code (using .OnSection of the dropdown). In order to make sure that the crosstab is always up to date after changes of the data or the [Control] worksheet, we call the sub CreateTextPivotTable within the event driven procedure Worksheet_Activate of the sheet [Pivot Table Risks]. Every time the sheet is activated, the crosstab will be updated.
That’s it.
The Pros
- It works (well, you expected that, didn’t you?)
- It is easy to implement and easy to use
- The layout of the crosstab can easily be changed
- It eliminates most of the disadvantages of the static formula approach (see the cons described in the recent post)
The Cons
- VBA necessary
- Some preparation of the workbook required, but by far less efforts than with the formula based solution
- Limited to exactly one filter. There is no option for a crosstab without a filter or more than one filter. This would be possible, of course, but I tried to keep it as simple as possible
- Error handling is next to nothing. For instance, the code will not check if it will overwrite data or formulas. There is no warning. You have to make sure that there is enough empty space right and below of the defined start cell of the crosstab
- The layout definition is flexible, but not very user-friendly. A user form with dropdown lists to change the layout and the formatting would be more convenient
The Performance
If you are using a more complex VBA procedure, the performance of the code is always an interesting topic. I did some stress testing. With a relatively small amount of data (150 data rows in the example workbook), the crosstab updates instantaneously. Using a database of 5,000 rows, the procedure takes 0.6 seconds, with 10,000 rows this increases to 1.2 seconds, with 65,000 data rows it takes even 6.4 seconds. Agreed, 6.4 seconds is everything else than a good user experience.
However, I do not think that matters in this specific case: unlike a real Pivot Table, we are not aggregating data. We are simply rearranging it and showing an enumeration in a tabular crosstab. From my point of view this wouldn’t make sense with a large database of 10,000 rows or more. Thus, performance shouldn’t be a problem.
The Download Link
Here is the Excel workbook for free download:
Download Pivot Tables_with_Texts – VBA Approach (Excel 2003 workbook, 121K)
Please be advised that the workbook is Excel 2003 file format, but I tested the code only with Excel 2010. If you encounter any problems with the file using Excel 2003 or earlier, please leave me a comment.
Acknowledgement
Many thanks go to Ulrik Willemoes, who was once more kind enough to spend some of his precious time reviewing my workbook and discussing it with me. As usual, Ulrik provided a couple of very interesting suggestions how the workbook could be improved. Many thanks, Ulrik!
I decided to save one of Ulrik’s best ideas for a follow-up post. So, if you liked this article, please stay tuned. There will be one more post on this topic coming soon.
Leave a Reply to Salim Cancel reply